Geographical Environment
时间:2023-03-23 15:48:01
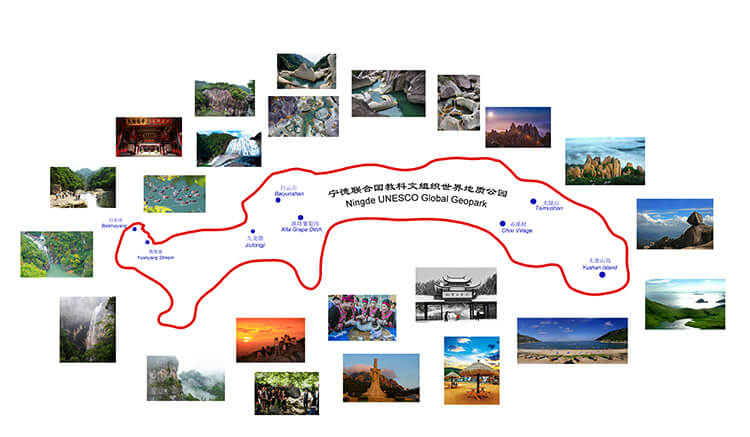
Ningde UNESCO Global Geopark, a large integrated geopark, characterizes the Late Mesozoic granite, volcanic rock geoheritages and modern river erosional landforms. It has both coastal and island landforms, abundant humanistic landscapes as well as blending with good ecological environment. The combination of a variety of landforms and landscapes reflects the complexity of its geological history.
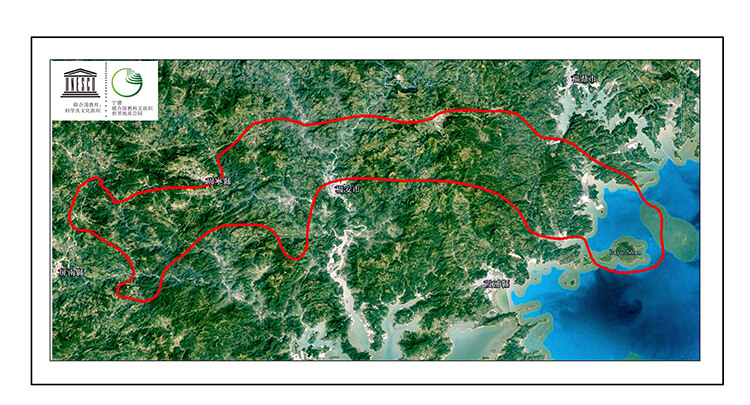
The Geopark is located in the mountainous and hilly region of Southeast China, and the terrain is generally high in the northwest and low in the southeast. The mountain range is controlled by tectonics, running generally in a North (North)-East direction, which mainly known as Jiufeng Mountain, Taimu Mountain Range. The highest peak of Dongshanding is 1479 m a.s.l. . The coastal areas are mainly high hills, forming a zigzagging coastline.
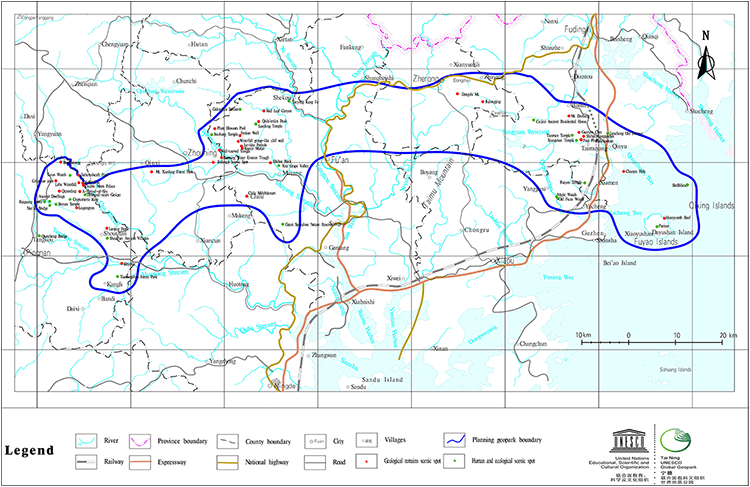
The coastline is very tortuous. The tidal flats are developed in the intertidal zone. The coastal islands are dotted with stars (Figure 1).
The Geopark is situated in the middle of the renowned Mesozoic-magmatic belt in Zhejiang Fujian and Guangdong Provinces, which is interpreted an evidence of an active continental margin of the marginal-Pacific. The Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous intermediate-acid volcanic rocks and intrusive rocks are widely distributed in the Geopark. The faults are mainly NE trending,while the NW and NE striking faults are secondary. In the Neoid Period, the Geopark is in the east mountainous area of Fujian Province and the landscapes are dominantly formed by water erosional type (Figure 2).