Biological Environment of Ningde UNESCO Global Geopark
编辑: 小编 时间:2023-07-04 10:43:57 浏览次数:
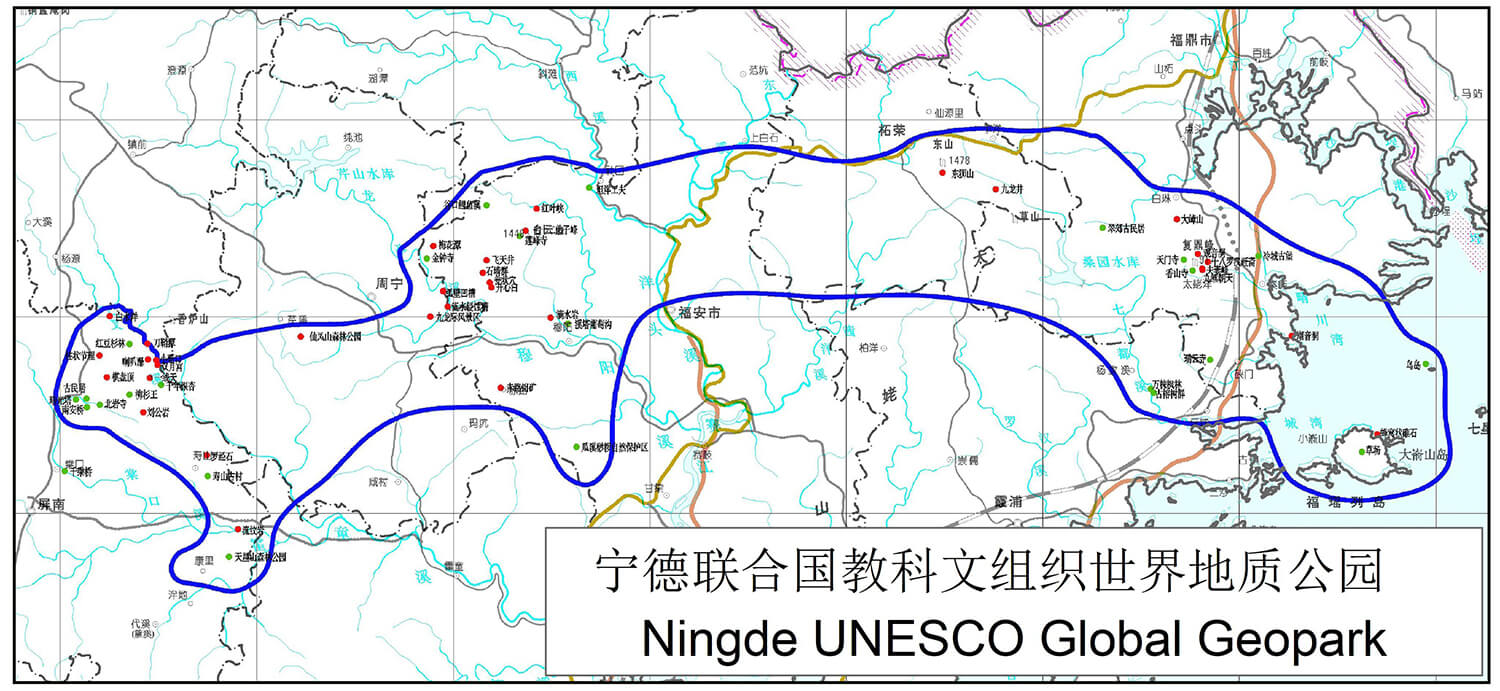
The NingdeGlobal Geopark has diverse geomorphological landscapes that are dominated by miarolitic granite, volcanic, canyon, and erosion riverbed landforms, accompanied by water, coastal, islands and marine erosion landforms. Of them, miarolitic granite landform dominates Taimushan in the Taimushanarea and Jiulongdong of the Baiyunshanarea; volcanic mountain landform mainly presents in Baishuiyang and Yiyang of the Baishuiyangareaand Baiyunshan in the Baiyunshanarea; erosional riverbed landform is seen in Baishuiyang of the Baishuiyangarea and Jiulongdong, Longtingxi of the Baiyunshanarea; and the coastal, island and marine erosion landforms occur in Qingchuan Bay and Fuyao Islands in the Taimushanarea , as well as canyon landform in Jiiulongji Gorge of Zhouning.
1.Biological Environment
1.1 Unique Biological Views
The Ningde Global Geopark is noted for its superior natural conditions and excellent biological environment. It boasts old banyan trees growing in the utmost northern latitude of the globe, natural mangroves and largest area of Chinese sweet gum in the south of Yangzi River. Furthermore, it is also well known for its flourishing cryptomeria with a history of one thousand years, water pine, a kind of relics plant in quaternary glacial epoch, rare tree species-Maire Yew and ginkgo, luxuriant tropical evergreen broadleaf forest and rare animals such as mandarin duck and monkeys etc. All these constitute an unique biological view. What is worth mentioning in the park are its other special biological scenic spots such as Putaogou (grape ravine) in Xita village,Muyun Town of She ethnic group, Tianhu grassland on Dayu Mountain, bird island and tea garden.
The diversified and rare feature of species of Ningde Global Geopark is rarely seen in the same latitude of the globe. It is closely related to its special geographical location and landform, which are shaped after long term’s geological function. Consequently, the diversified and rare feature of species of Ningde Geopark not only enjoys significant biological value but also displays the principal impact of geological function.
1.2 Plant Resource
The park boasts superior natural conditions and sound biological environment. The forest coverage ranges from 72% to 90%. Main categories of primary vegetation are ever-green broadleaf forest. It is categorized into East China humid forest area of three Chinese regions of vegetation. The types of vegetation include most categories of plants in China’s regions with subtropical ocean monsoon climate. It is characterized by the typical feature, diverse quality and systematic character of subtropical region.Main subcategories of vegetation in Baishuiyang Scenic area are temperate coniferous forest, warm-hot savanna forest, deciduous broadleaf forest, evergreen broadleaf forest, bamboo, deciduous broadleaf shrub, typical evergreen broadleaf shrub, shrub grassland etc. They include 43 formations and 212 associations. The determined names of vascular plants in the park are classified into 162 families, 508 genera, and 855 species, rare and endangered plants 11 families, 18 genera and 26 species. Among them 18 species are under the first and second national protection level, 13 species are key provincial protection plants.
The vegetation in Baiyunshan Scenic area is classified into six typical categories such as evergreen coniferous forest, bush, evergreen broad-leaved forest, mixed forest, bamboo and grass. The park boasts 1015 species vascular plants. Among them, pteridophyta are classified into 28 families, 41 genera and 65 species; gymnosperm is divided into 9 families, 16 genera and 23 species; angiosperms amount to 136 families, 531 genera and 927 species. Three of them are plants at the first national protection level; fifteen are plants at the second national protection level. Rare and endangered ones amount to 12 families, 21 genera and 24 species.
Vegetation of Taimushan Scenic area is classified into 4 categories: broadleaf forest, coniferous forest, bamboo and bush. The vascular plants in the park amount to 491 species. Among them, gymnosperm is classified into 9 families, 18 genera and 29 species; angiosperms amount to 65 families, 194 genera and 462 species. Three of them are rare and endangered plants at the second level national protection. It is noted for diversified category of bamboo.Among them main ones are Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro, bitter bamboo, Wong Chuk, dendrocalamopsis, arundo donax, rare species such as square bamboo, black bamboo and inverted bamboo. Diversified and multicolored azalea of the Scenic area is also well-known and becomes one of its main features.
1.2.1 Representative Plants
Evergreen Broadleaved Forest
Evergreen broadleaved forest exist in the monsoon subtropics area, dominated by fagaceae, lauraceae, theaceae, magnoliaceae broadleaved evergreens trees. The structure compares with the tropical rain forest to be simple, the bryophyta is rich under the forest. The area and the growth condition of evergreen broadleaved forest in China come first in of whole world.
Coniferous and Broadleaved Mixed Forest
It is a transitional form between boreal forests and broadleaved forests. Usually composed by the Quercus, Acer, Tillia trees and the Picea, Abies, Pinus trees. It forms a discontinuous mixed forest belt in Eurasia's high latitude. Mainly distributes in the Northeast mountainous region in China. There were the small area in the southern mountainous region
Bamboo Forest
The bamboo forest is the community dominated by single species. It is widespread in subtropics region of China. The moso bamboo forest is the biggest among them, and generally distributes below the elevation 900 meter. In some places, the bamboo mixes the junction with other trees.
1.2.2 Protected or Endangered Plant Species of the Geopark
Currently, the geopark has 3 endangered plant species which are under state first-grade protection such as Taxus mairei and Ginkgo biloba; 15 species under state second-grade protection such as Fokienia hodginsii, Cryptomeria fortunei, Glyptostrobus pensilis and Taiwania cryptomerioides; and some species under provincial priority-ranked protection such as Cinnamomum micranthum, Phoebe zhennan and Rhododendron simsii.
Glyptostrobus pensilis (Staunton ex D. Don) K. Koch. Chinese name: Shui Song. English name: Canton water pine. Belong to Taxodiaceae. First grade protected plant in China Conifer tree, 20~30 m tall and 60~120 cm DBH. Crown conical, lower branches spreading, upper ones more erect. Air roots grow from lateral roots, and spread up to 6 ~7 m around the base of tree. Bark thick, greyish-brown, longitudinally issured. Shoots of two kinds, long and short. Leaves delicate green when young, rich brown in autumn; those on the long shoots overlapping and scale-like; those on the short shoots needle-like, sickle-shaped, enlarged at the base. Pollen cones terminal on short shoots. Ovulate cones terminal on lateral shoots, pear-shaped or ovate. Cone scales obovate, thin, bearing wart-like, sub-apical teeth and a small, triangular mucro above their centre. Seeds ovate or oblong, thin-coated and terminated by a hatchet-shaped wing. It blazoned in the Cretaceous Period and the Cainozoic Era in Northern Hemisphere, exterminated from Europe, America, Japan and other region after late Quaternary ice age. Mainly exists in the mountains below elevation 1000 meters of Zhujiang low, damp, riparian areas of Guangdong and Minjiang Watershed of Fujian.
Taxus wallichiana (Pilg.) Rehd. var. mairei (Lemee et Levl.) Cheng et L. K. Fu. Chinese name: Nanfang Hongdoushan. English name: maire yew. Belong to Taxaceae. First grade protected plant in China, VU This evergreen tree, with its thick foliage and red arillate seeds, is an excellent and graceful conifer tree for urban afforestation and is of great medicinal properties. It exist widely in subtropical area of China. However, the tall Maire yews have been destoried seriously decades ago. It is scattered over Fujian and can be seen in the moso bamboo forests.
Cryptomeria fortunei Hooibrenk. Chinese name: Liu Shan. English name: China Cedar. Belong to Taxodiaceae A conifer tree, reaching up to 50 m tall and 4 m DBH, with red-brown bark which peels in vertical strips. The leaves are arranged spirally, needle-like, 0.5 ~ 1 cm long; and the seed cones globular, 1.8~2 cm diameter with about 20 scales. The timber is light and soft, the grain straightens out, the structure is fine, can supply for building, bridge, ship, papermaking. The bark is used as medicine to cure ringworm. May also extract the tannin extract. And it is an excellent gardening tree. Distributes in Zhejiang, Fujian, Guangdong and Guangxi and the Yangtze River watershed.
Ginkgo biloba L.; Chinese name: Yin Xing, Gongsun tree, White fruit; English name: ginkgo, maidenhair tree. Belong to Ginkgoaceae, EN in IUCN red list, first grade protected plant in China, EN in CSRL A deciduous tree, native to China only. It is the only surviving species of the class Ginkgoatae and is considered a living fossil. It is of great scientific value on the study of the gymnospermous phylogeny, the evolution of plants and systematic taxonomy.
1.3 Animals
Main subcategories of vegetation in the Ningde global Geopark are temperate coniferous forest, warm-hot savanna forest, deciduous broadleaf forest, evergreen broadleaf forest, bamboo, deciduous broadleaf shrub, typical evergreen broadleaf shrub, shrub grassland etc. They include 43 formations and 212 associations. The determined names of vascular plants in the park are classified into 162 families, 508 genera, and 855 species, rare and endangered plants 11 families, 18 genera and 26 species. Among them 18 species are under the first and second national protection level, 13 species are key provincial protection plants.
According to world zoogeographical division and China’s zoogeographical division, most of animals in the park are classified into species of middle China genus of oriental kingdom. Some of them belong to species of south China and some others are palaearctic. The whole area boasts over 2000 species of wild animals. There are over 700 vertebrates. Among them there are over 70 species of mammals, 324 species of birds, over 100 reptiles, over 30 species of amphibians and over 600 species of fish. Invertebrates amount to more than 1300. The park boasts various rare, endangered and protected animals. Among them animals in the first category of national protection include Clouded Leopard, Boa and Chinese sturgeon; in the second category of national protection include Serow, Rhesus Macaque , Large Indian Civet,Malayan pangolin, Mandarin Duck, Common Kestrel, Blake Kite , tiger frog , silver pheasant , Alcedo;kingfishers , Silver-eared Leiothrix, Syrmaticus , and Tufted deer etc Sea area in Fuding is rich in fish resource.
1.3.1 Protected Animal
Aix galericulata (Linnaeus), Chinese name: Yuan Yang, Government duck; English name: mandarin duck; French name: canada mandarin. Belong to Anatidae, second grade protected animal in China. It is a medium-sized perching duck, 39~45 cm long with a 65~75 cm wingspan. The adult male is a striking and unmistakable bird. It has a red bill, large white crescent above the eye and reddish face and "whiskers". The female is with a white eye-ring and stripe running back from the eye, but is paler below. In the wild, Mandarin Ducks breed in densely wooded areas near shallow lakes, marshes or ponds. They nest in cavities in trees close to water. They are migratory. Mandarins feed by dabbling or walking on land. They mainly eat plants and seeds. They feed mainly near dawn or dusk, perching in trees or on the ground during the day. Mandarins may form small flocks in winter, but rarely associate with other ducks.
Macaca mulatta (Zimmermann). Chinese name: Mi Hou; English name: Rhesus macaque. Belong to Cercopithecidae. second grade protected animal in China Macaca mulatta is a monkey, 45~64 cm length, with 19~32 cm long tail, and weigh 5.5~12 kg. Males are somewhat heavier than females. They have grizzled-brown fur dorsally, with the fur on the ventrum being slightly lighter in color. The hair is short on the head. The face and buttocks of adults are red. Although rhesus monkeys live in groups, they are not territorial. Macaca mulatta lives in a wide range of habitats, and shows a great deal of adaptability. Macaca mulatta is omnivorous, and often eat roots, herbs, fruits, insects, crops, and small animals. Mainly distributes in southern China, such as Guangdong, Guangxi, Yunnan, Guizhou etc. Also distributes in Burma, Nepal, India, Bangladesh, Pakistan.