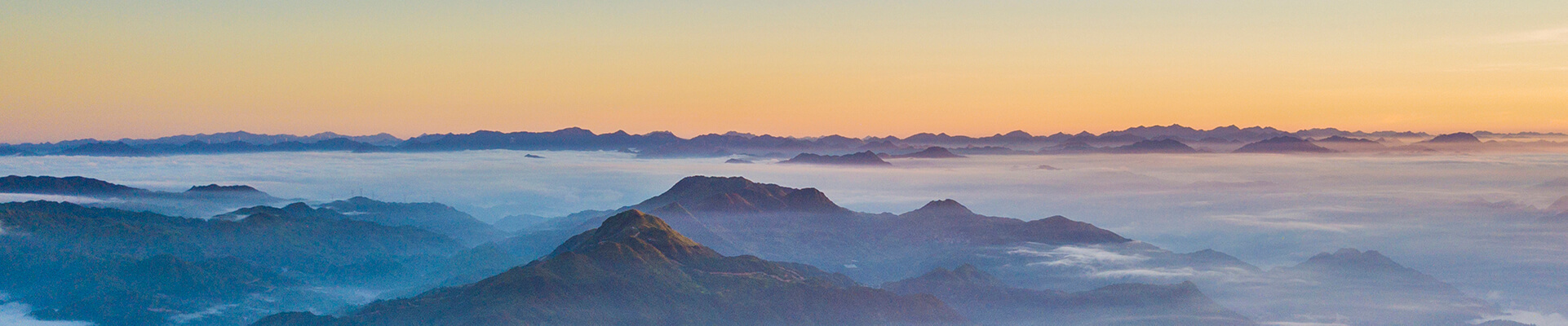
Geotourist Route of the Taimushan Scenic Spot
编辑: 小编 时间:2023-07-03 18:38:25 浏览次数:
The miarolitic granite-formed peak cluster-stone egg landform in the Taimushan is the best one in the coastal areas of southeastern China and thus is the typical representative of this kind of landform.Various peak cluster are distributed in the Taimushan Scenic area. They are composed of rock peaks, rock forts, rock walls and rock pillars. The peak clusters are towering. The standing pillars look just like forests. These vivid landforms together with various shaped stone eggs construct a lovely scenery painting
1 Granite Peak Cluster(Eighteen Arhats Hurrying for Dinner)
The peak cluster is a common granite landform. The vertical joints are developed and the horizontal ones undeveloped here. After the granite exposed on the earth’s surface, affected by the long-term weathering and other geological processes, the cluster peaks would be formed, whose peaks are completely separated but the base fully connected together. It represents the earlier stage of granite landform development. Looking at this peak cluster, it seems like 18 arhats in different shapes hurrying for dinner.

2 Three sets of joints in miarolite
Affected by the later tectonic movement, there are two sets of vertical joints (strike directions of NW320 ° and NE60° ) and one set of horizontal joint developed in the miarolite in Mount Taimushan. These joints control the development of granite peak cluster-spherical landform in Mount Taimushan. After later weathering denudation, fluvial erosion and gravitational collapse along the vertical joints, stone columns, castle- and wall-like granite landforms are occurred, and the horizontal joints control the formation of the spherical granite landforms on the tops of the stone columns, castle- and wall-like granite landforms.

3 Granite Pictographic Stone(Couple-like Peak)
The pictographic stone is a common granite landform. The horizontal and vertical joints are developed here. After the rock exposed on the earth’s surface, the spherical weathering caused by temperature change and other geological processes was occurred and the spheroid topography would be taken place, so the various pictographic landforms can be formed in granite. This pictographic peak looks like a couple here. So it is named as the Couple-like Peak.

4 Jionts
Joint is a crack in rock, which is one of the most developed structures in the crust. A joint indicates a crack with no significant displacement on both sides. In the cooling process of magmas, the primary joints are always developed in granite. Now, this deep crack belongs to a primary vertical joint in the granite.

5 Granite Pictographic Stone(Cat-and mouse-shaped Stone)
The granite pictographic landform is a common phenomenon. Here is the top of Tianzhu peak, where the horizontal and vertical joints are developed. After the rock exposed on the earth’s surface, the spherical weathering would be occurred and the smooth spheroid topography would be developed under the effect of long-term temperature change and other geological processes. The granite stones here look like a cat playing with a mouse.

6 Joints in Granite
The vertical joints are greatly developed in granite here. Controlled by two sets of vertical joints, the joints in granite here become wider and wider under the effect of the long-term weathering. So this huge granite body looks like three nearly 10-meter-long parallel stone plates.

7 Granite Pictographic Stone(Monkey-shaped Stone)
The granite pictographic landform is a common phenomenon. The horizontal and vertical joints are developed here. After the rock exposed on the earth’s surface, the effect of the long-term spherical weathering would be occurred along the joints, under the effect of the later gravitational collapse, the various lifelike pictographic landforms would be occurred. This granite pictographic stone here seems like a monkey holding a mirror to dress up.

8 Narrow Gorge
Narrow gorge is a typical geological landform, characterized by steep slope and narrow passage, whose bottom width is nearly equal to the upper part. The narrow gorge is generally related to the structural and fluvial processes. However, the narrow gorge here is, different in origin from these above, derived from the widening of the vertical joints in granite under the long-term weathering. Due to the later gravitational collapse, there are three large granite stones hanging up in the narrow gorge. When visitors go through the gorge, you should stoop down three times.This gorge about 30 m long.

9 Granite Pictographic Stone (Orangutan-like Stone)
When the vertical and horizontal joints are developed, it is easy to form various interesting pictographic landforms. Looking at this cliff, you can find an orangutan-like picture on the cliff, which is a masterpiece by nature. When the granite exposes on the Earth surface, affected by the long-term spherical weathering and other geological processes, the rock surfaces become round and smooth, which forms the head of the orangutan. The vertical joint surface becomes a huge cliff, the two horizontal cavities on the surface resulted from the weathering of the two miarolitic cavities, which are the orangutan’s eyes.

10 Narrow Gorge(Seven-star Cave)
Narrow gorge is a typical geological landform, characterized by steep slope and narrow passage, whose bottom width is nearly equal to the upper part. The narrow gorge is generally related to the structural and fluvial processes. However, the narrow gorge here is different in origin from these above, derived from the widening of the vertical joints in granite under long-term weathering. The gorge is about 40 m long and less than 1 m wide. There are 7 huge stones hanging on the upper part of the gorge, like 7 stars inlayed in the fissure, which come from the gravitational collapse.

11 Granite Landscape Group(Carps Jumping into the Sky)
Granite landscape group is composed of granitic spheroid topography and peak cluster landform, generally developed in the vertical and horizontal joint-developed granite areas. When such granite exposes on the Earth surface, they will be suffered from a long-term temperature-induced weathering and other geological processes, the spherical weathering leads to the formation of spheroid topography. Being the vertical joints developed, the granite peak cluster landform will be occurred, with separated peaks and a common base, which represents the earlier stage of granite landform development. The scenery here is spectacular, the peak cluster extends over thousand meters, like a school of carps jumping out of the water and up into the sky. Here is the most magnificent landscape.

12 Scouring Ditch Group
The scouring ditch group is a unique landform in granite. After the granite exposes on the Earth surface, the granite surfaces become smooth under the effect of long-term weathering and erosion. Because of the abundant rainfall here, many ditches have been occurred on the smooth surfaces scoured by rain water. These ditches are closely arranged, which look like a magnificent waterfall flying downward, this is one of the specific landscapes in Mt. Taimushan Scenic Area.

13 Joints in Granite
There are several parallel cracks in the granite at front of the Baiyun Temple, named primary granite joints. They are originated from the cooling process of magmas, the strike is NW 265 ° . Additionally, the sheet-like weathering is developed on the granite surfaces, ultimately the stones will become round, called the typical spherical weathering.

14 Fuding Peak
This is the summit of Mt. Taimushan Scenic Area, with an elevation of 917.3 m. When the vertical and horizontal jointdeveloped granite exposes on the Earth surface, it will be suffered from a long-term temperature-induced weathering and other geological processes, the spheroid landform will be formed. The erosion surfaces will be scoured by rain water and the brown ditches will be occurred. Looking at the Fuding Peak, it looks like a reversed ancient Chinese vessel.

15 Horizontal Joints
The horizontal joints are well developed in the miarolite in Mount Taimushan, sometime intruded by veins or with crystal cavities, which were mainly formed in the cooling and condensing period. Together with two sets of vertical joints, they cut the granite into rock blocks in different sizes. It plays an important controlling role in the formation of the miarolite peak cluster and stony egg landform in Mount Taimushan.

16 Granite Peak Cluster
The granite peak cluster is commonly seen in the granitedistributed area where the primary joints are developed. The peak cluster is the group of the cone-shaped peaks, of which the bases are connected together, this landform represents the earlier stage of granite landform development. The peak cluster here could be divided into two types based on the difference of distribution, height and exposed duration. The right one is bigger and more complete, and the left more cracked, it indicates that the latter was exposed for a longer time, the later gravitational collapse is more obvious.

17 Miarolite
The miarolite is major landscape-forming rock in Mount Taimushan, formed about 90 Ma ago. It is a kind of special hypabyssal granite with deep source origin. The SiO2 content is generally over 76%. Due to its high viscosity, the gases contained in magma were incapable to escape away in the process of condensation and crystallization near the earth’s surface, so the numerous cavities were formed in miarolite. The special cavity structure would occur in the later period of the magma crystallization.

18 Stone Basin, Stone Mortar
Granite surface is easy to be eroded by the rainfall. The weathered and loose feldspar and quartz grains on the surface will be transported away. A pit would be gradually formed in the strongly eroded spot and linear running water convergent place. The accumulated water in the pit will strengthen the physical and chemical weatherings on the pit sidewall. Then the pit will be gradually expanding, forming round or oval stone basin or mortar. This stone column shows three round stone mortars developed along the running water line.

19 Natural bridge-Rock Arch
After the weathering and flowing water erosion, a rock wall of about 50-60 cm thick was formed between two vertical joints (NE50° ) in the miarolite. The rock wall bottom, under the effect of weathering and rainwater erosion, was gradually thinned and finally penetrated through, forming a rock arch of about 4 m long and 3 m high. Then, a natural bridge—rock arch is finally shaped.