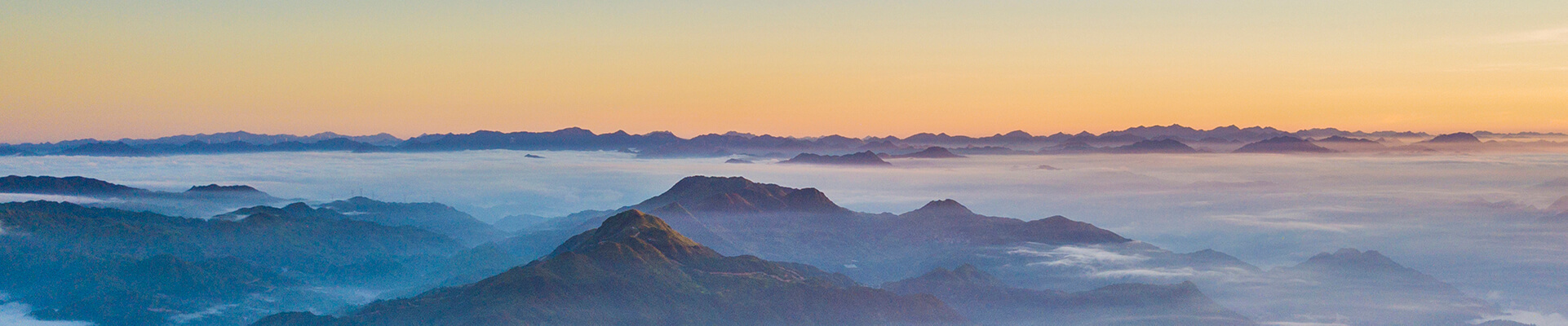
Geotourist Route of the Baishuiyang Scenic Spot
编辑: 小编 时间:2023-07-03 18:17:42 浏览次数:
The riverbed of the Baishuiyang River is basal rock wide and flat with a length of 2 km. The river is divided into upper, middle and lower parts. The widest riverbed is in the middle part and is 182 m in width. It forms a vast shallow water square with an area of near 40,000 m 2 and therefore is a wonderful place to enjoy with water.Water flow erosion is very strong in the Baishuiyang and therefore the landforms in the area are distinguished. The main flow erosion-generated landforms include flat bedrock-formed riverbed, erosional terrace, wall-curved river bank, rocky ripple marks on bedrock, water erosion-generated trough, flow side erosion-generated cave, and pothole. Therefore, the Baishuiyang River is a wonderful place for scientific popularization and understanding the importance of geological processes.
This smooth tabular rock has many holes and troughs on its surface, which have different size and depth. Someone might have already thought that the tabular rock is quite similar with the riverbed of the Baishuiyang River. Yes, it is really the old bed of the Baishuiyang River. The tectonic movement (about 2.6 million years ago) caused the slow uplift of the earth crust in the area and thus the rise of the riverbed of the Baishuiyang River. The later down cutting of the water has made a new riverbed for the river. While, the old riverbed now is exposed and is in a level 1.5-2 m higher than the new one. You can image the great power of the water erosion just from this case.

Why is the level of the rock platform by the Xianpa River higher than that of the current riverbed? Geologically, this platform, together with the above sediments, is called river base terrace. Actually, it was once the riverbed of the Xianpa River in the ancient time. Later tectonic movement (2.6 million years ago) has led to the gradual uplift of the earth crust in the Baishuiyang area. The long-term down-cutting erosion resulted in the lowering and narrowing of the riverbed. Today’s level of the riverbed is 1.5-2 m lower than that of the original one. The remained old riverbed became this flat river terrace. Seeing this you cannot help exclaiming the power of the geological process.

Do you know what the collapsed rock block is? Vertical joints and fractures have developed in the volcanic rocks. The whole rocks in the cliff wall often collapsed and fell along the planes of break structures due to gravitation process. The collapsed rock blocks accumulated on the base of the cliff or on the gentle slope face. These are the collapsed rock blocks. This lucky peach standing by the Xianpa River is a huge collapsed rock block of volcanic agglomerate fallen from the opposite cliff wall. It looks just like a huge peach bringing lucky to the guests.

This widespread flat rocky riverbed with covering clear shiny ripple water is the famous scenery, Baishuiyang River, a shallow water square. The formation of the scenery is contributed to the multi-geological factors, such as rock attitude, lithology, geological structure, hydrological dynamics, etc. The Baishuiyang riverbed is composed of orthophyre, which intruded along volcanic bedding near the ground level during the magma activity about 100 million years ago and formed a tabular subvolcanic rock body parallel to the ground. The rock is quite integral and very uniform. With the uplift of the earth crust and the down cutting of the river, the orthophyre has exposed. Dense horizontal joints parallel to the bedding and multi-directional vertical joints and fractures have developed in the orthophyre. The weathering and water erosion have flaked away the rocks along the horizontal joints and gradually formed this flat rocky riverbed. The continuous uplift of the earth crust since 2.6 million years ago and long-term water erosion and down cutting resulted in the lowering of the river base. The old riverbed became the river base terrace lying on the two sides of the river. Later, the down cutting power of water became weak due to the stable earth crust and a very slow rise of the Baishuiyang area. The weak water down cutting could only produce water-eroded trough and pothole. Instead, the water lateral erosion was dominant at this stage. The strong lateral erosion has formed wide concaved riversides at the cross of the two brooks and in some portions of the up- and down-river. The extending of the riverbed is consistent with the tabular orthophyre body, forming this wide, flat and mirror-like Baishuiyang scenery.

How was this deep groove formed? Initially, the riverbed developed a group of N40 ° E-oriented fissures due to the tectonic movement of the Earth’s crust. Because the fractured portion is a weak park of the rock, long-term water erosion has resulted in the formation of this deep groove in the fractured part of the riverbed, 1-1.5m wide.

This is a small waterfall. A group of NW-oriented joints developed in the bedrock-formed riverbed. The long-term flow erosion along the joints has formed a 40m-long, 1m-high step. The water falling from the step forms this cascade.

During volcanic eruption, a great number of gases accumulated on the top of underground molten magma. This can cause a huge blast due to great pressure. After the blast, the remained magma has cemented the broken pieces of the adjacent rocks. Suchformed rock has broken sharp fragments embedded in the cement that has the same composition as the fragments.

The gallery bridge in wood arch is the assembling of bridge, corridor, pavilion and temple into an organic whole, it need not any iron nail, link-up each parts only by the wooden tenon and mortise, that shown the precise design of construct craft, is unique in the world. The gallery bridge in wood arch recorded the magnificent articles of Chinese bridge history. In October 2009, the Traditional design and practices for building Chinese wooden arch bridges was inscribed on the List of Intangible Cultural Heritage in Need of Urgent Safeguarding UNESCO.

How were these shuttle-shaped troughs on the riverbed formed? The NE-strike fractures and NW-strike fractures are both developed in the rocks of the riverbed due to tectonic movements. Some of the fractures have the same directions with the water current and thus have undergone long-term water erosion. This formed concave surfaces on the soft portions of the riverbed, which gradually become these water-eroded troughs.

The waterfall is situated at the junction of the middle and lower Baishuiyang River where the river-course is relatively narrow and water flow is thus concentrated. The relative strong water erosion results in the formation of an inclined bedrock-composed riverbed, about 50m long and over 100m wide, which looks just like a huge sliding board. You can slide from the ramp without any harm to your naked skin. It is a scared but no dangerous play. What a fantastic sight it is.

Why does the Bird’s-nest Rock have five concaved caves at the cliff base and show a wavy appearance in its cliff-wall? The lateral erosion of water formed these wavy appearance and horizontal caves. During the stage when the earth crust was stable, the water erosion was characterized by lateral erosion, which concaved the cliff wall. While during the uplift stage of the earth crust, the down cutting of river has brought the lateral erosion and so produced concave marks to a different level of the wall. The lateral erosion-induced concave marks of different levels representing different stages made the cliff-wall have a S-shaped wavy appearance. The five semi-circle concave caves arranged side-by-side at the base of the cliff are the horizontal caves formed by the long-term lateral erosion of water during stable earth crust stage, which look like girl’s skirt and thus are also called Multi-folded Rock.

How was this Gauze-cap-like Rock formed? The rock originally developed many NE-strike joints, fractures and faults. In the places where fractures and faults were densely distributed, the rocks were broken up and washed away by water current. While the rocks were kept in the place where fractures and faults were rare. With the uplift of the earth crust, down-cutting erosion of water and lowering of the river base, the remained rocks has formed a rock wall on the middle of the riverbed, extending in the direction parallel to the water flow. The further down-cutting and lateral erosion of the water have narrowed and modified the rock wall into an isolated rock pillar, which became a firm rock in the mid-river.

The volcano eruption-formed rocks are different in composition, texture, and the development of joints and fissures. Therefore, they have different behaviors under water erosion, gravitational collapse, and weathering processes. The rocks that can resist the weathering form the peaks. A peak cluster is composed of several pillar-like, fort-like peaks that are connected on their bases.

The bamboo forest is the community dominated by single species. It is widespread in subtropics region of China. The moso bamboo forest is the biggest among them, and generally distributes below the elevation 900 meter. In some places, the bamboo mixes the junction with other trees.

Why does the riverbank here have a curved appearance? The tectonic movement has led to the development of joints and fractures in the volcanic rocks that construct the riverbank. Later weathering has further enlarged the joints and fractures and formed many sheet tensile-fractures on the rock surface. The long-term water lateral erosion has caused the flake off of the rocks in the riverbank wall and formed this curved riverbank, which is a distinct landform sight.

Rocks often fall off from the joints and fissures of the steep cliff due to gravitation. These fallen rocks are called collapsed rock body. Here is a so-formed collapsed rock body. The big rock block has a volume of 6×5×3 in meter, while the small one is 2×1×1 meter. They are scattered on the river sides.

How were these ripple marks on the riverbed formed? The attrition between shallow water flow and the riverbed can form crescent flow-waves that are vertical to the flow direction. The flow-wave has a characteristic that the wavetrough is more powerful than the wave-peak in making down-cutting erosion. The erosion on the riverbed is mainly performed by flow waves other than carried sand and mud because the shallow water can only carry limited solid materials. After such long-term erosion, the base rocks of the riverbed became concaved along the troughs of the wave. This gradually formed many water erosion-induced ripple marks on the riverbed, having a shape similar with the flow-wavy. In addition, the development of the crossed NE- and NW-strike faults in the riverbed also helps the formation of the ripple marks. The ripple marks are linked end-by-end, just like many regularly arranged huge fish scales in the clear water. It looks like a huge auspicious dragon swimming with the wave and welcoming the guests.